- April 22, 2024
- Posted by: Shane Daly
- Categories: Options Trading, Stock Trading, Trading Article


You’re probably aware that both put options and short selling can help you reap benefits when stock prices decline. But do you know which strategy works best for you?
Put options offer a safety net by defining your potential losses, while short selling can be a high-risk, high-reward strategy. Let’s dig into these strategies, weigh the risks and rewards, and help you decide which approach aligns best with your investment goals.
Understanding Short Selling
It’s essentially borrowing securities, selling ’em, and hoping to buy ’em back at a lower price. Here’s the breakdown of how it operates, the risks involved, and its relevance in varying market scenarios.
What is Short Selling?
It’s a tactic where you’re selling securities that you’ve borrowed, to make a profit if their price drops. Frequently used by institutional investors, it’s a bearish strategy. To execute a short sell, you’ll need a margin account, given that you’re essentially borrowing the stock to sell it, planning to repurchase it at a lower price later on.
However, you should be aware of the potential risks. You’re exposing yourself to limitless losses because if the stock’s price soars instead of dropping, you’ll need to buy it back at a steeper price.
Here’s a brief explanation of the terms involved:
| Term | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Short Selling | The act of selling borrowed securities |
| Margin Account | An account required for short-selling |
| Unlimited Losses | The risk linked with short-selling |
| Bearish Strategy | A strategy that profits from declining prices |
| Institutional Investors | The usual users of short-selling |
The Mechanics of Short Selling
First, you’ll need a margin account to short-sell, as you’re essentially borrowing securities to sell with the intent of repurchasing them later at a lower price.
It’s important to keep an eye on market conditions. The goal is to profit from declining prices, but if prices rise, losses can be virtually limitless.
This is where the concept of risk management enters. By careful strategy formulation, these risks can be reduced, but remember, short selling isn’t suited for all. It demands a substantial understanding of the market dynamics and a capacity for risk-taking.
Risks of Short Selling
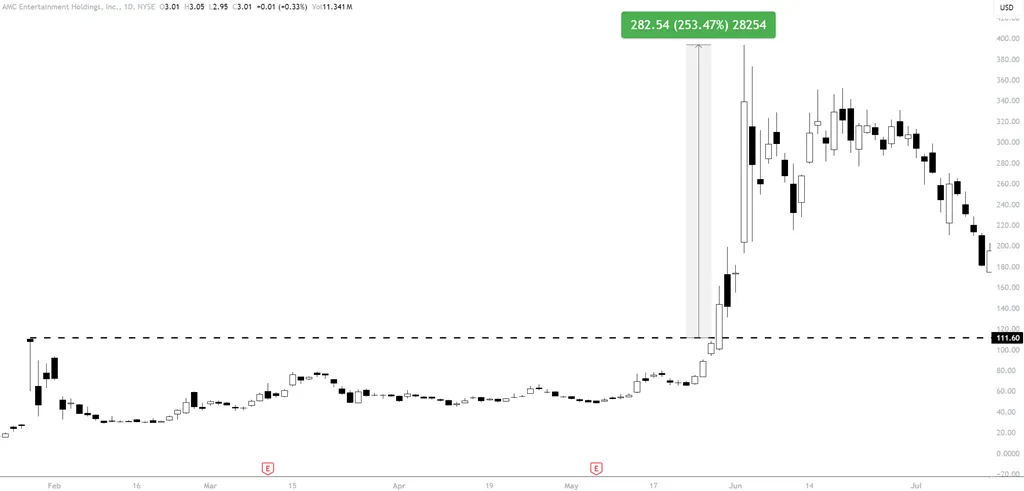
When short selling, you’ve got to know its potential for limitless losses if the borrowed security’s price unexpectedly goes up. A short squeeze risk is real – a rising stock price can force you to buy back shares at a loss. And if losses surpass the margin requirements, you’re looking at a margin call, meaning you’d need to come up with more capital.
Market dynamics are key to understanding since timing is an important part of this strategy. Short selling isn’t for everyone; you need to seriously consider if you’re up for handling these risks.
Short Selling in Different Market Conditions
In a bear market, short selling can be quite profitable. That said, it’s important to consider things like volatility, market cycles, and short interest.
Here’s what you have to do:
- Figure out where the market’s headed. Bearish trends usually offer the best chances.
- Keep an eye on the short interest. If it’s high, that could mean a short squeeze is coming.
- Don’t forget about risk management. This means setting stop-loss orders to keep potential losses in an acceptable range.
In short, to successfully short sell, you need a deep understanding of the market and strong risk management strategies.
Exploring Put Options
Put options grant the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell an asset at a specific price (known as the strike price) before a set expiration date. They’re essentially a bet that a stock or other asset’s price will fall, offering a way to profit from a downturn in the market.
 Consider this example: You buy a put option for a certain company’s stock at a strike price of $50, expiring in a month. If the stock price drops to $30 within that month, you can buy shares at the lower price and sell them at the strike price, netting a $20 profit. However, if the stock price remains above the strike price, the option becomes worthless and you lose the premium paid for it.
Consider this example: You buy a put option for a certain company’s stock at a strike price of $50, expiring in a month. If the stock price drops to $30 within that month, you can buy shares at the lower price and sell them at the strike price, netting a $20 profit. However, if the stock price remains above the strike price, the option becomes worthless and you lose the premium paid for it.
Put options have risks. The most prominent is the potential loss of the entire premium if the stock price doesn’t drop below the strike price. However, they offer benefits too, such as providing a way to hedge against potential losses. If you own a stock and buy a put option at the same time, any loss on the stock is offset by the gain on the put option.
Put options are a versatile tool for traders and investors alike. They offer a great way to bet on declining prices, protect existing investments, and potentially return substantial profits.
What are Put Options?
Put options, in essence, are like insurance policies. They provide you the option, but not the obligation, to sell an asset at a predetermined price within a set period. They’re leveraged in hedging strategies to capitalize on a drop in an asset’s price, such as a stock index.
- Strike price: It’s the price you’ve locked in for selling the asset.
- Option expiration: It’s the timeframe you’ve to exercise your selling right.
- Time decay theta: It’s how your put option’s value shrinks over time.
Think of it this way: you’re betting on a horse race, except the horse is the price of a stock. If the stock’s price falls (the horse loses the race), you make money. If it doesn’t (the horse wins), you only lose what you paid for the put option (the bet).
It’s all about managing risk. The strike price is your safety net, the option expiration is your window of opportunity, and the time decay theta is the ticking clock that could either spell profit or loss.
How Do Put Options Work?
Put options aren’t as complicated as they might seem. Here’s how they work: you get the right to sell a security at a fixed price, within a set time. You’re essentially buying this right, which costs you a premium. This strategy is typically used when you’re assuming the security’s price will go down, increasing your chances of making a profit.
Your loss is limited to the premium you’ve paid. This provides a safety net against big losses. So, put options serve two main purposes; they let you speculate on price decreases and control potential losses.
Risks and Benefits of Put Options
These options can cap your risk at the premium paid and act as a shield against downside risk, but they also hinge on precise forecasts of price drops for profitability.
Let’s consider these points:
- Market Cap: Bigger companies with a higher market cap usually have increased trading volume, enhancing liquidity and execution.
- Portfolio: Put options can safeguard your portfolio from short-selling risks and offer a cushion against market fluctuations.
- Predictability: Put options demand a robust prediction of market movements. If you’re wrong, you could lose the entire premium paid.
Make sure you’ve got a handle on this before adding put options to your investment strategy.
Using Put Options for Hedging
By hedging with put options, you’re essentially putting a safety net under your investment portfolio. Here’s why: if the market starts to decline, your put options will be compensating for losses elsewhere.
The premium for the option? That’s all you risk losing, making this a smart choice for safeguarding your investments.
Comparative Analysis: Put Options vs Short Selling
We’re going to explore the risk vs profit potential. We’ll see how market conditions can favor each one, and what you need to know about executing these strategies.
| Strategy | Description | Risk | Profit Potential |
|---|---|---|---|
| Put Options | An investment strategy where you bet that a stock’s price will go down. | Limited to the premium paid. | High if the stock price plummets. |
| Short Selling | Involves borrowing a stock you don’t own, selling it, and then hoping to buy it back at a lower price. | Can lose more than initial investment if the stock price rises. | Profit from the price difference between selling and buying back. |
Market conditions, they can favor put options or short selling. If volatility is high, it can be a good time for put options. Why? Because volatility increases the price of options. But beware, it can also increase your risk.
Practically speaking, executing these strategies requires some expertise. You need to know when to enter and exit a position, how to manage risk, and how to navigate the technicalities of the options market or the rules of short selling.
Got all that? Great. This is just a high-level view, but hopefully, it helps you understand the basics of put options and short selling. Now, you’re on your way to making more informed investment decisions.
Risk and Profit Potential
While both put options and short selling can yield profits from falling market prices, they’re different in terms of risk and potential returns. Put options, especially those in the money, are generally safer. Your losses are only limited to the premium you’ve paid.
Let’s compare the two strategies:
- Short selling can lead to unlimited losses, a risk not present in put options.
- Put options provide leverage, letting you control a larger amount of shares with less capital. On the other hand, short selling requires a margin account and larger capital.
- For bearish strategies, put options profit when the stock drops below the strike price. Short-selling profits when the stock price decreases.
These three points can help guide you in determining which one is suitable for you.
Market Conditions Favorability
Remember, market conditions can sway the appeal of put options and short selling. In erratic markets, put options can be an account saver. They’re preferred due to the limited risk and adaptability across varying assets. You’ve got the right to exercise this within a set period, letting you manage trading costs effectively.
Short selling can be your strategy in long-lasting bear markets with steady downward trends. But be aware, that it needs precise timing and continuous market monitoring. Knowing market conditions and trends is key when picking between put options and short selling.
Each strategy has its benefits, so choose based on your risk tolerance and market knowledge.
Practical Considerations in Execution
When you’re weighing up put options against short selling, you’ve gotta consider the practical aspects of pulling off these strategies, each having unique risk-reward profiles.
- Put options act like a safety buffer – they limit your losses to the premium you’ve paid. They’re great if you’re a bit more risk-averse and like knowing your max risk from the get-go.
- Short selling is a different beast. It could give you massive losses, as there’s no ceiling on how high a stock’s price can go. It also means having a margin account and dealing with higher costs, so it’s better suited for those with a bit more trading experience under their belt.
- Both strategies have the same goal: making a profit when prices dive. But how you go about them is different. Choose carefully, keeping in mind your comfort with risk, experience, and resources.
Impact of Volatility on Both Strategies
When volatility is up, put options get pricier due to higher premiums. that is not always a bad thing. This heightened volatility could boost the chance of the underlying asset reaching your strike price.
On the flip side, short selling is more complex with high volatility. Prices can fluctuate, exposing you to potential margin calls and losses. In low volatility times, short selling may appear easier, but remember, limited price movement can also cap your profits.
Applications in Portfolio Management
Short selling is an aggressive tactic where you borrow shares you don’t own, sell them, and hope to buy them back at a lower price. You’re betting that the stock will drop in price. If it does, you’ll profit from the difference.
On the other hand, put options are defensive. You’re buying the right to sell a stock at a certain price. If the stock’s price falls, you can still sell it at the higher price you locked in. You’re protected from big losses. Mixing these methods can diversify and balance your portfolio. They work together to protect your investments.
Let’s apply these concepts. Say you’ve got a feel that a stock’s going to fall. You could short-sell it and if you’re right, you’ll make money when you buy it back cheaper. But what if you’re wrong and the stock rises?
Cue the put option.
You could use it to sell that stock at a higher price, avoiding a big loss.
Short Selling for Aggressive Strategies
You can exploit bearish positions on individual stocks or the whole market, but it’s a high-risk, high-reward approach.
Here are the main points to consider:
- Short selling can lead to large profits if prices plummet as anticipated.
- It demands vigilant tracking and risk handling to dodge significant losses if prices ascend.
- Experienced traders who can handle these risks will find this strategy most suitable.
In short, short selling can be a strong weapon in your investment strategy.
Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Identify a stock you anticipate will decline in price.
- Borrow the stock from a broker and sell it immediately.
- Wait for the stock price to fall.
- Buy back the stock at a lower price and return it to the broker.
- The difference between the sale price and the buyback price is your profit.
Put Options for Defensive Strategies
 When you’re managing your investments, short selling can be an aggressive method to bet on falling prices. On the other hand, put options provide a more defensive strategy. Buying put options gives you the right, not an obligation, to sell your assets at a set price. Think of it as an insurance plan when the market takes a downturn, helping to keep your portfolio’s value intact.
When you’re managing your investments, short selling can be an aggressive method to bet on falling prices. On the other hand, put options provide a more defensive strategy. Buying put options gives you the right, not an obligation, to sell your assets at a set price. Think of it as an insurance plan when the market takes a downturn, helping to keep your portfolio’s value intact.
Including put options in your portfolio management is you thinking about the worst-case scenario. It’s a great way to reduce losses when the market’s future is uncertain.
Blending Both for Diversification
To diversify your portfolio and manage risk, you could blend both put options and short-selling strategies. These two methods can help you stay afloat in bearish market conditions and hedge against downside risk.
- Diversification: Combining put options with short selling offers a mix of risk limitation and high-profit potential. You’re not putting all your eggs in one basket and you’re also opening up the possibility for substantial gains.
- Adaptability: This dual strategy lets you adjust to changing market dynamics and investor sentiment. If the market veers in an unexpected direction, you’ve got the tools to adapt.
- Enhanced Performance: Using both strategies can boost your overall portfolio performance and risk management. You’re not just relying on one strategy to do all the work.
When you’re using put options, you’re buying the right to sell a stock at a predetermined price. You’re essentially betting that the stock’s price will fall, and if it does, you can sell it at a higher price than its current market value. So, you’re limiting your risk while also potentially making a profit.
On the other hand, short selling involves selling a stock you don’t own, to buy it back later at a lower price. This strategy can be profitable if the stock’s price decreases but can also result in losses if the price increases. It’s a riskier strategy, but it can pay off if used wisely.
By blending these two strategies, you’re creating a balanced portfolio that allows for both risk management and profit potential. The blend provides a buffer against market volatility and potential losses, while also allowing you to profit from price movements in both directions.
Advanced Insights in Put Options and Short Selling
Ever thought about how traders’ mindset impacts short selling? Or how do shifts in implied volatility affect put options?
Short Selling and Market Psychology
Understanding the play of market psychology in short selling and put options can enhance your investment choices. Market psychology moves investor sentiment, shaping the outcome of your bearish tactics.
- Fear and greed influence market activity. Consider widespread panic – market prices could nosedive, making short selling a profitable move.
- A herd mentality often directs the market. When most investors are selling, it’s smart to think about a short sell or put option.
- Importantly, stay alert to your own biases. Things like loss aversion and confirmation bias can muddle your thinking, leading to irrational choices.
Put Options and Implied Volatility Trends
Let’s focus on the role of implied volatility trends. These trends can significantly affect the success of your put options strategy.
Implied volatility goes up, and the premium of put options goes up. This is a sign the market’s uncertainty is growing. During these times, you’ll notice put the options are pricier.
It’s important to monitor these trends. They can help you estimate potential profits. They also help fine-tune the timing and impact of your strategy. Even a small change can have a big effect on your put options’ value.
Here’s how implied volatility trends can change your strategy:
| Implied Volatility | Put Options Premium | Market Uncertainty |
|---|---|---|
| High | High | Increased |
| Low | Low | Reduced |
| Rising | Increasing | Rising |
| Falling | Decreasing | Falling |
Future Trends and Evolving Landscape
Let’s look at future trends and changes in the world of put options and short selling. Specifically, the rise in the use of automated trading strategies.
- Regulatory shift: New rules and regulations are changing the game. They’re affecting how much trading happens and how easy it’s to trade. You’ve got to stay in the loop and be ready to change your strategies.
- Technology integration: Big data and machine learning are making it easier to make decisions and manage risk. You can’t afford to ignore these tools.
- Innovation in financial instruments: We’re seeing new kinds of derivatives that offer new opportunities for sophisticated strategies. You’ll want to keep an eye on these developments.
The world of trading is always changing. To stay on top, you’ve got to keep learning, be ready to adapt, and be open to new ideas.
Conclusion
In conclusion, you’ll see profits from put options and short selling when stock prices take a hit. However, it’s crucial to remember that put options offer a safeguard, capping potential losses.
On the flip side, short selling could result in sizable losses if it’s not monitored correctly. Always take into account market conditions, volatility, and your personal risk capacity when deciding on your approach.
Keeping yourself educated and strategic is key to boosting your investment profits.
