- October 12, 2023
- Posted by: Shane Daly
- Categories: Options Trading, Trading Article

Looking to maximize your profits in a bullish market? Wondering when and how to use bull call spreads?
In this article, we will explore the benefits and considerations of employing bull call spreads in a bullish market. By strategically combining call options, you can limit losses while capitalizing on a gradual increase in stock prices.
Understanding the Basics of Bull Call Spreads
A bull call spread is an options trading strategy that aims to benefit from a stock’s limited increase in price. By using two call options with different strike prices, this strategy allows you to limit losses while capping gains.
One advantage of a bull call spread is that it’s cheaper than buying an individual call option. It also limits the maximum loss of owning a stock to the net cost of the strategy.
There are also disadvantages.
Any gains above the strike price of the sold call option are forfeited, and the gains are limited due to the net cost of the premiums.
To implement this strategy effectively, you should have a moderately bullish outlook.
Overall, a bull call spread offers moderate profit potential while managing risk.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Implementing Bull Call Spreads
When implementing a bull call spread, you can benefit from limited gains in a bullish market while also reducing the cost compared to buying an individual call option. Below is a table outlining the pros and cons, as well as the risk and profit trade-off, of implementing a bull call spread strategy:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Limited gains from an upward stock price | Forfeiting gains above the strike price of the sold call |
| Reduced cost compared to buying a call | Limited gains due to the net cost of the premiums |
| Limits maximum loss to the net cost | Trade-off between risk and potential profit |
The market forecast for a bull call spread is a moderately bullish outlook. The strategy performs best when the stock price rises above the strike price of the short call at expiration. Changes in stock price have a positive impact on the spread, while changes in volatility have minimal effect.
At expiration, the potential positions created depend on the stock price’s relation to the strike prices. Overall, implementing a bull call spread allows for limited gains in a bullish market while managing costs and risks effectively.
Comprehensive Overview of Bull Call Spreads
Here are four key points to understand about bull call spreads:
- Bull call spreads are most effective in optimal market conditions where the stock price is expected to rise moderately.
- This strategy helps manage risk by limiting losses BUT capping potential gains.
- Compared to buying an individual call option, bull call spreads are generally cheaper and offer a higher chance of making a larger percentage profit.
- It’s important to consider other bullish strategies, such as bull spreads, bull put spreads, and butterfly spreads, to determine the best approach for your investment goals.
Practical Examples and Potential Profit/Risk Analysis
Suppose you are interested in Company XYZ’s stock, which is currently trading at $100 per share. You have a moderately bullish outlook on the stock and want to use a bull call spread to limit your risk while still benefiting from a potential price increase.
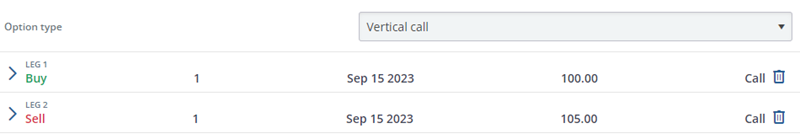 Bull Call Spread Details:
Bull Call Spread Details:
- Buy a Call Option (Long Call):
- Buy 1 XYZ 100 Call Option with a strike price of $100.
- The premium for this long call option is $3.30 per share.
- Sell a Call Option (Short Call):
- Simultaneously, sell 1 XYZ 105 Call Option with a strike price of $105.
- The premium received for this short call option is $1.50 per share.
Calculations:
- Net Cost (Debit) of the Bull Call Spread:
- Cost of Long Call: $3.30
- Premium Received from Short Call: -$1.50 (negative because you receive this premium)
- Net Cost = $3.30 – $1.50 = $1.80 per share
Maximum Profit and Loss:
- Maximum Profit: The maximum profit for this bull call spread is the difference between the strike prices minus the net cost of the spread.
- Maximum Profit = ($105 – $100) – $1.80 = $3.20 per share
- Maximum Loss: The maximum loss is equal to the net premium paid to establish the spread.
- Maximum Loss = $1.80 per share
Breakeven Stock Price at Expiration:
To calculate the breakeven stock price at expiration, you add the strike price of the long call to the net premium paid:
- Breakeven Stock Price = Strike Price of Long Call + Net Premium Paid
- Breakeven Stock Price = $100 + $1.80 = $101.80
Outcome Scenarios at Expiration:
At expiration, several scenarios can occur:
- If the stock price is at or below $100, both the long and short call options expire worthless, and you incur a maximum loss of $1.80 per share.
- If the stock price is between $100 and $105, the long call is exercised, and you have a long stock position. The short call expires worthless. Your profit or loss depends on the stock’s price relative to your breakeven point of $101.80.
- If the stock price is above $105, both the long and short call options are exercised. You have a long stock position, but you also have an obligation to sell stock at $105, which may result in a capped profit.
This example demonstrates how a bull call spread allows you to profit from a moderate rise in the stock price while limiting both potential gains and losses.
Implementing The Bull Call Spread Strategy
To effectively implement the bull call spread strategy, it’s important to consider factors such as strike prices, premiums, and potential profit limitations. When applying this strategy, there are practical applications and implementation strategies that can help optimize your risk management and profit potential.
Here are some key points to consider:
Market conditions: Before employing a bull call spread, assess the market conditions and identify a bullish trend in the underlying stock. This strategy performs best in a gradually rising market.
Strike prices: Selecting the appropriate strike prices for the long and short call options is essential. The long call should have a strike price below the current market price, while the short call should have a higher strike price.
Premiums: Evaluating the premiums of the call options is crucial for determining the net cost of the strategy. The premium received from selling the short call should offset the premium paid for buying the long call.
Profit potential: It’s important to recognize that the profit potential of a bull call spread is limited. The maximum profit is achieved when the stock price is above the strike price of the short call at expiration, but it’s capped at the difference between the strike prices minus the net cost of the spread.
Impact of Stock Price and Volatility Changes on Bull Call Spreads
When evaluating the impact of stock price and volatility changes on a bull call spread, it’s important to consider how the spread’s price reacts to these factors.
| Factor | Impact on Bull Call Spread |
|---|---|
| Stock Price Change | Rises as stock price rises, declines as stock price falls |
| Volatility Change | Changes very little |
| Risk/Reward Tradeoffs | Understanding price dynamics helps with informed decision-making |
| Forecast Analysis | Crucial for accurate predictions |
| Cash Flow Timing | Timing of cash flows should be considered when implementing strategy |
The price of a bull call spread rises as the stock price rises and declines as the stock price falls. It has a net positive delta, which estimates how much the option price will change as the stock price changes.
However, the change in option price is generally less than dollar-for-dollar with the change in stock price.
On the other hand, the price of a bull call spread changes very little when volatility changes.
Other factors such as stock price and time to expiration remain constant. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed risk/reward tradeoffs and conducting accurate forecast analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the drawbacks of a Bull Call Spread?
One primary drawback of a bull call spread is that it caps your potential gains. While it limits your losses as well, any price increase in the underlying asset beyond the strike price of the short call option will not result in additional profits. Additionally, transaction costs, such as commissions, can impact the overall profitability of the strategy. Finally, it’s crucial to choose the right strike prices and expiration date, as an incorrect selection can lead to suboptimal results.
What is the difference between a Bull Call Spread vs. Bull Put Spread?
The choice between a bull call spread and a bull put spread depends on your market outlook and risk tolerance. A bull call spread is used when you expect a moderate rise in the underlying asset’s price. It involves buying a call option with a lower strike price and selling a call option with a higher strike price. A bull put spread is employed when you anticipate a modest increase in the asset’s price. It consists of selling a put option with a higher strike price and buying a put option with a lower strike price.
What are the Pros and Cons of a Bull Call Spread?
The main advantage of a bull call spread is that it offers limited risk, as your maximum loss is capped at the net premium paid. It also costs less than buying a single call option. However, the strategy comes with the drawback of limiting potential gains beyond the short call’s strike price. This capped profit potential may not be suitable for those seeking higher returns, and transaction costs should be factored into the analysis.
What is the Profitability of a Bull Call Spread in a Rising Market?
A bull call spread is designed to be profitable in a rising market. It allows you to benefit from a moderate increase in the underlying asset’s price. As long as the stock price rises above the strike price of the short call at expiration, you can realize a profit. However, keep in mind that the profit potential is limited due to the capped gains.
How do I Profit with a Bull Call Spread?
To profit with a bull call spread, you should initiate the spread when you anticipate a gradual price rise in the underlying stock. Your goal is to have the stock price move above the strike price of the short call option by expiration. If this occurs, the spread will result in a profit equal to the difference between the strike prices, minus the net premium paid. This profit is realized if the stock price is at or above the short call’s strike price at expiration.
Conclusion
Utilizing bull call spreads in a bullish market can be a wise strategy to maximize profits and minimize losses. This options trading strategy allows investors to benefit from a gradual increase in stock prices while also managing risk.
By combining call options with different strike prices, traders can navigate periods of high volatility and make informed decisions. The power of bull call spreads lies in their ability to provide a comprehensive overview of potential profit and risk analysis, making them a valuable tool in a trader’s arsenal.
