- January 26, 2023
- Posted by: Shane Daly
- Category: Trading Article

Options are financial instruments that give investors the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price and date. They can be a useful tool for managing risk in a diversified investment portfolio.
If you are a seller of options, this can provide an income stream or be used to offset any losses in holdings and to profit from sideways market action.
What is Risk Management
Risk management involves reducing potential losses by recognizing potential risks in advance. This can include diversifying your portfolio, hedging strategies, and proper capital allocation. We can also use options to help mitigate risks in our portfolios regardless of the market climate. At Netpicks, we like to use strategies that can produce profit in five different ways.
What is Hedging
Hedging in the financial markets refers to the practice of using financial instruments, such as options or futures contracts, to reduce the risk of potential losses from fluctuations in asset prices. This can be done by buying or selling securities to offset potential losses from other positions in the portfolio. For example, if an investor is long on a stock, they may buy put options on that stock as a hedge against potential losses from a decline in the stock price.
Hedging can be used to manage the risk of individual investments or the overall risk in a portfolio. It is a common practice among investors and financial institutions to help reduce the impact of market volatility and protect against potential losses.
It is important to carefully consider the risks and potential rewards of hedging before implementing any strategies.
Use A Covered Call Strategy
One way to use options to manage risk is by implementing a covered call strategy. This involves holding a long position in an underlying stock and selling a call option on that stock.
 If the stock price rises above the strike price of the option, the investor can sell the stock at the strike price, realizing a profit from both the stock and the option. However, if the stock price falls, the investor can keep the stock and let the option expire worthless, limiting the potential loss.
If the stock price rises above the strike price of the option, the investor can sell the stock at the strike price, realizing a profit from both the stock and the option. However, if the stock price falls, the investor can keep the stock and let the option expire worthless, limiting the potential loss.
Covered Call Example
An investor holds 100 shares of XYZ Corporation, which is currently trading at $50 per share. The investor believes that the stock price will eventually rise in the future, but wants to limit the potential loss if the stock price falls. The trader sells one call option on XYZ Corporation with a strike price of $52 and an expiration date in three months. Premium received is $2.00/share or $200/contract.

As the seller of the call option, you don’t want the price of the stock to gain much traction to the upside. In a perfect world, the expiration date comes, stock is below the strike of $52.00 and you keep the premium received as income. Because the buyer of the call option does not exercise their right to buy your stock, you continue to hold it.
If the price rises above $52.00, the contract could be exercised. This is not a bad thing if you were considering selling the stock at this price point.
In this example, the covered call options strategy allows the investor to participate in the potential upside of the stock, while also having some income if the price drops.
Protective Puts
Another risk management strategy using options is the protective put. This involves holding a long position in a stock and buying a put option on that stock. If the stock price falls, the investor can exercise the put option and sell the stock at the strike price, limiting the potential loss.
 If the stock price rises, the put option will expire worthless, but the investor can still profit from the stock.
If the stock price rises, the put option will expire worthless, but the investor can still profit from the stock.
Protective Put Example
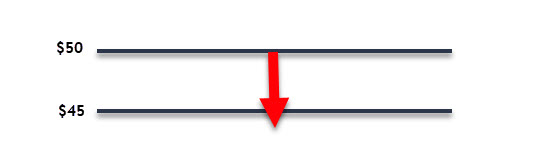
An investor holds 100 shares of XYZ Corporation, which is currently trading at $50 per share. The investor is concerned that the stock price may fall but wants to retain the potential for profit if the stock price rises. The investor buys one put option on XYZ Corporation with a strike price of $45 and an expiration date in three months.
If the stock price falls below $45, the trader can exercise the put option and sell the stock at $45 per share, realizing a profit of $500 from the option plus the difference between the stock price and the strike price. If the stock price does not fall below $45, the option will expire worthless and the investor can keep the stock, retaining the potential for profit if the stock price rises.
 In this example, the protective put allows the investor to protect against potential losses if the stock price falls, while still retaining the potential for profit if the stock price rises.
In this example, the protective put allows the investor to protect against potential losses if the stock price falls, while still retaining the potential for profit if the stock price rises.
More Complex Strategies
Options can also be used in combination with other securities to create more complex strategies. For example, a bull call spread involves buying a call option on a stock with a low strike price and selling a call option on the same stock with a higher strike price. This can provide limited downside protection and potential for profit if the stock price rises.
Quick FAQS
Options trading can be used to manage risk in a diversified investment portfolio.
Covered call options allow investors to participate in potential upside while limiting potential losses if the stock price falls.
Protective puts involve holding a long position in a stock and buying a put option on that stock, allowing for limited downside protection.
Bull call spreads involve buying a call option on a stock with a low strike price and selling a call option on the same stock with a higher strike price, providing limited downside protection and potential for profit if the stock rises.
It is important to carefully consider the risks and rewards of options trading before implementing any strategies.
Wrap Up
Options can be a valuable tool for managing risk in a diversified investment portfolio. By implementing strategies such as covered calls and protective puts, investors can protect their portfolios against potential losses while still participating in the market upside movement. Hedging strategies are very popular with those who have substantial holdings but is also available to the smaller retail trader.
As always, it is important to carefully consider the risks and potential rewards of options trading before implementing any strategies.
Don’t Miss This
You don’t need to have tens of thousands of dollars to start trading options.
With One Day Options Trading Strategy, you can make money whether the stock market goes up, down, or even sideways.
Check out our free Options guide called 8 Minute Options Cookbook to learn more
