- April 15, 2024
- Posted by: Shane Daly
- Category: Trading Article

Understanding the Outside Bar Failure pattern is helpful for short-term trading strategies when dealing with market volatility and reversals. This pattern helps identify failed breakouts and predicts price reversals aligning with the main trend.
To recognize this pattern on price charts, look for an outside bar followed by a reversal bar in the opposite direction. The reliability of this pattern is higher in trending markets with strong momentum. To enhance your strategy, waiting for confirmation signals and placing stop losses beyond the outside bar is recommended.
Understanding Outside Bars
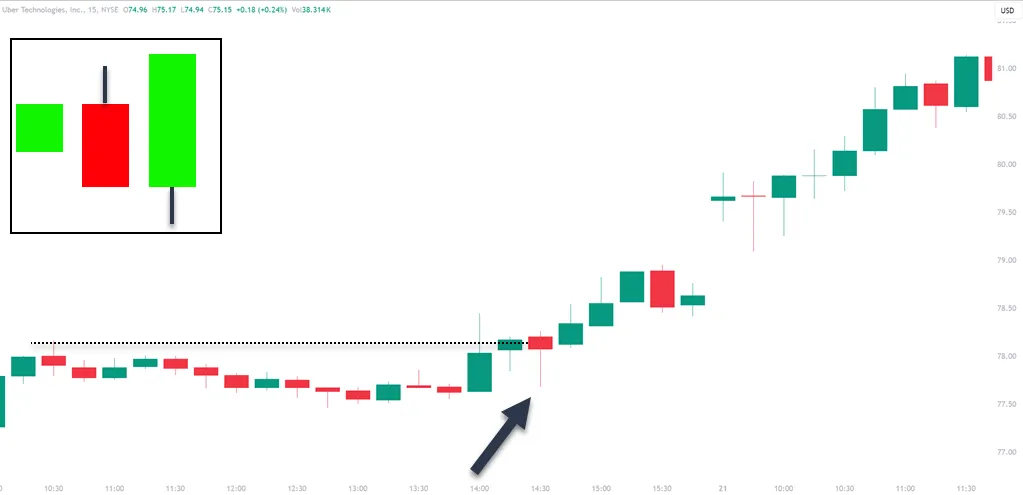
Understanding outside bars is key in trading. This pattern occurs when a bar’s highs and lows exceed the previous bar’s. This clear distinction on price charts is a sign of potential shifts in market sentiment.
Contrary to popular belief, outside bars aren’t random fluctuations. They are good at hinting at possible trend reversals or continuations. Traders can use this knowledge to make trading decisions based on other analyses they’ve done and their overall understanding of price action.
For example, bullish outside bars show a higher high and low than the previous bar. This could indicate a bullish reversal or the continuation of an upward trend. These bars, with their emotional and unpredictable nature, help in identifying potential reversals and managing risks effectively.
Outside Bars = Lower Timeframe Pullback
An outside bar is essentially a pullback on a lower time frame when talking about an uptrend. This is more obvious when the outside bar closes red.
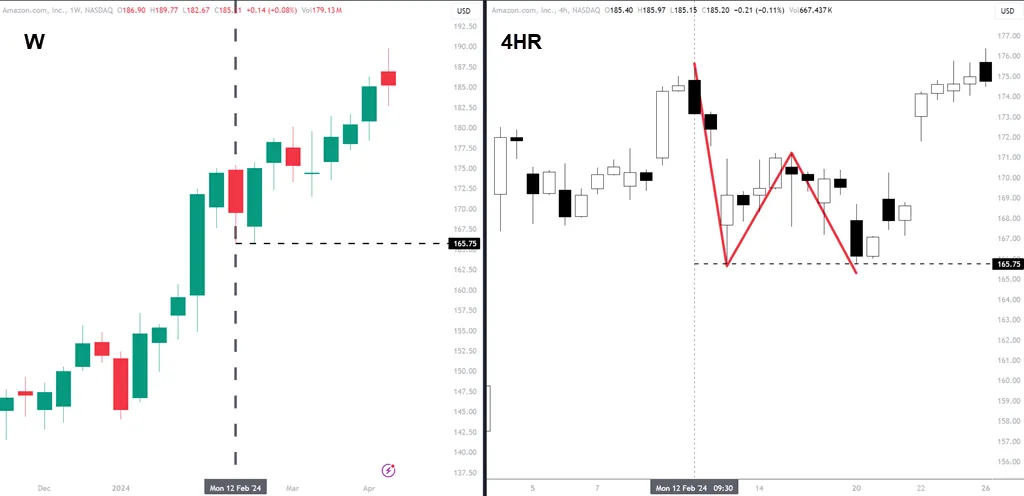
When using candlestick patterns such as this, remember that if you change time frames, the pattern changes. As you gain experience, you can look at a smaller time frame, such as this four-hour chart, and envision that it is an outside pattern on the weekly.
Concept of Pattern Failures
Understanding pattern failures is essential for improving your trading outcomes. These failures occur when expected price movements based on specific patterns don’t happen as anticipated, influencing your trading choices. Managing these events is key to reducing risks and implementing successful contrarian trading methods.
By recognizing pattern failures, you can adjust your strategies according to market sentiment, and oftentimes set yourself up in a good trade. When people are wrong, people react. Often that will be trades exiting positions that go against them which will fuel the trade in your trade direction. It’s the “trapped traders” event that occurs.
Your trading psychology plays a role in how you handle pattern failures. While it’s natural to feel emotional when trades don’t go as planned, maintaining a disciplined approach is vital for your long-term success. Acknowledging pattern failures empowers you to navigate challenging market conditions while staying focused on your trading objectives.
Incorporating effective risk management practices is vital when facing pattern failures. Setting stop-loss orders and managing your position sizes can help minimize potential losses and safeguard your capital.
Anatomy of an Outside Bar Failure
When you encounter an outside bar failure in contrarian trading, it can indicate a potential market reversal and lead to significant price movements. An outside bar pattern that isn’t confirmed by the price action suggests a change in sentiment and can be a signal for traders to pay attention to.
As the market fails to follow through after an outside bar forms, it shows that there’s indecision among traders. This indecision reflects a battle between bulls and bears for control, highlighting a pivotal moment for decision-making.
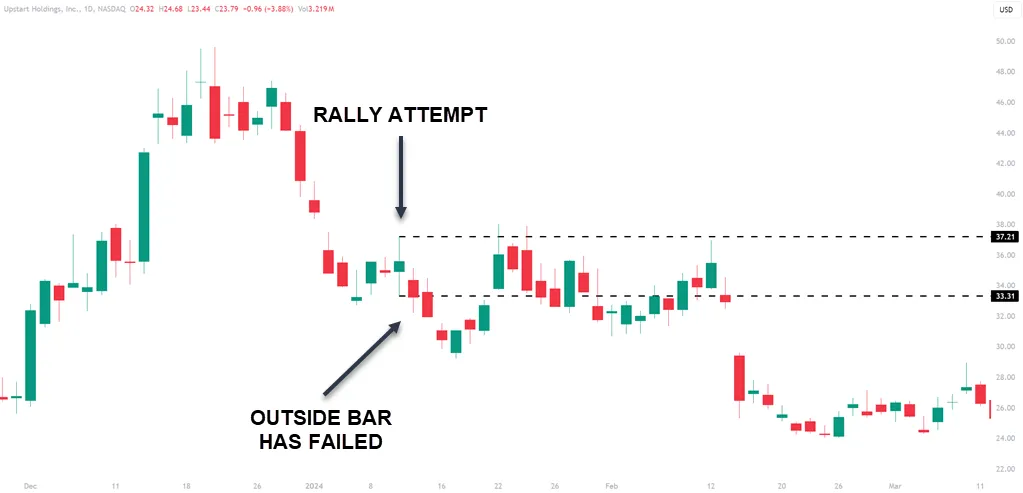
Traders who focus on price action study outside bars for specific characteristics that may hint at potential failures. By recognizing these signs, traders can plan their trades effectively and be prepared for possible shifts in the market.
Outside bar failures often precede noticeable price movements in the opposite direction, offering profitable trading opportunities for those who can spot them.
Market Context and Outside Bar Failures
Understanding outside bar failures in contrarian trading is heavily influenced by the market context. You need to grasp market psychology to interpret these patterns effectively. Trends play a vital role in determining the significance of outside bar failures. Traders need to assess the strength and direction of the current trend to understand the potential impact of these patterns accurately.
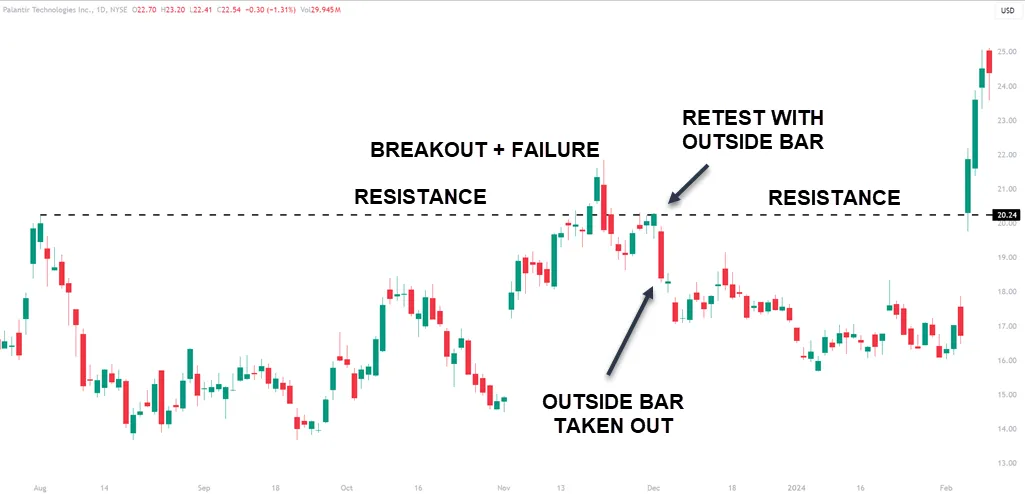 Additionally, identifying key support and resistance levels is essential when analyzing outside bar failures. These levels serve as markers where price often reacts, helping traders anticipate potential reversals more efficiently.
Additionally, identifying key support and resistance levels is essential when analyzing outside bar failures. These levels serve as markers where price often reacts, helping traders anticipate potential reversals more efficiently.
Trend analysis is a cornerstone in recognizing the context of outside bar failures. Focus on identifying clear trends that provide a backdrop for these patterns, signaling a possible shift in market sentiment. By adding trend analysis into their strategy, traders can better understand the implications of outside bar failures and make trading decisions that are aligned with the prevailing market direction.
Paying attention to market psychology, trend analysis, and support/resistance levels is vital for successfully navigating outside bar failures in contrarian trading.
Trading Strategies for Outside Bar Failures
When trading outside bar failure patterns, you need to have a well-thought-out plan for entering and exiting trades. Timing your entry accurately is key. Look for signals that confirm the outside bar failure before jumping into a trade. This might involve waiting for the low/high of the outside bar to be broken or retested before making a move.
Managing your risk is equally important. Use stop-loss orders to protect yourself from significant losses if the market goes against your trade. Consider your position size about the risk you’re willing to take on in your overall account.
Follow your trading plan when executing trades. Stick to your predetermined entry and exit points, avoiding impulsive decisions driven by short-term market fluctuations. By mastering entry timing, risk management, and trade execution, you can improve your chances of success when trading outside bar failure patterns.
Let’s go over a trading strategy you can use as a framework for your design of a strategy.
Outside Bar Failure Contrarian Trading Strategy
Entry Rules
- Identify a clear trend in the market (uptrend or downtrend).
- Look for an outside bar that forms against the prevailing trend.
- Wait for the outside bar to close, confirming the pattern.
- Enter a trade in the opposite direction of the outside bar if the next 1-2 candles break above the low (for a bearish outside bar) or high (for a bullish outside bar) of the outside bar.
Exit Rules
- Set a profit target based on a multiple of the outside bar’s range (e.g., 1.5 times the range).
- Place a stop-loss order just beyond the high (for a bearish trade) or low (for a bullish trade) of the outside bar.
- If the trade reaches the profit target, exit the position.
- If the stop-loss is triggered, exit the position to minimize losses.
Risk Management
- Risk no more than 1-2% of your trading account on each trade.
- Adjust position size based on the distance between your entry point and stop-loss.
- Consider using a trailing stop to lock in profits as the trade moves in your favor.
Confirmation and Filters
- Use volume indicators to confirm the validity of the outside bar failure. Look for low volume on the outside bar and higher volume on the reversal.
- Incorporate moving averages (e.g., 20-period and 50-period) to gauge the strength of the trend and potential support/resistance levels.
- Consider the overall market sentiment and economic events that may impact the asset you’re trading.
Timeframe and Markets
- This strategy can be applied to various timeframes (e.g., 5 minutes, hourly, daily) depending on your trading style and preferences.
- The Outside Bar Failure Pattern can be used in different markets, including stocks, forex, futures, and options.
Remember to backtest this strategy using historical data and adapt it to suit your risk tolerance and trading style. As with any trading strategy, it’s essential to continue learning, refining your approach, and incorporating advanced concepts as you gain more experience in the markets.
Trade Examples
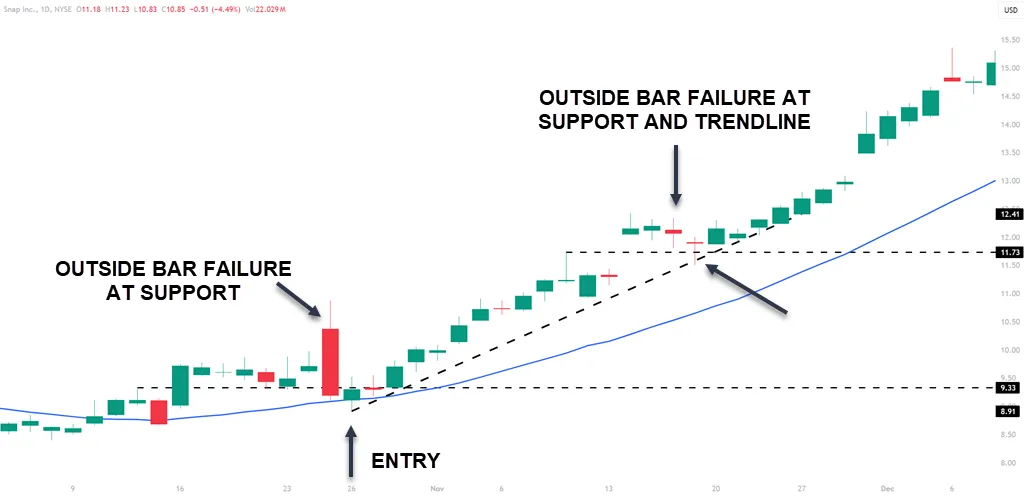
Uptrend defined by the 20 SMA slope upwards. The first trade has a large outside bar failure at support and the moving average. Price reclaims the low and you place a buy stop over the candlestick that breaks above the low.
The second trade has a gap up, a pullback to support, and a rising trend line. Buy stop the high of the candle that breaks the low of the outside bar for a long trade.
This setup works to the downside as well. This chart is a 30-minute chart and the moving average is generally sloping downwards. The outside bar fails at resistance and the next candle is the setup and trigger candle.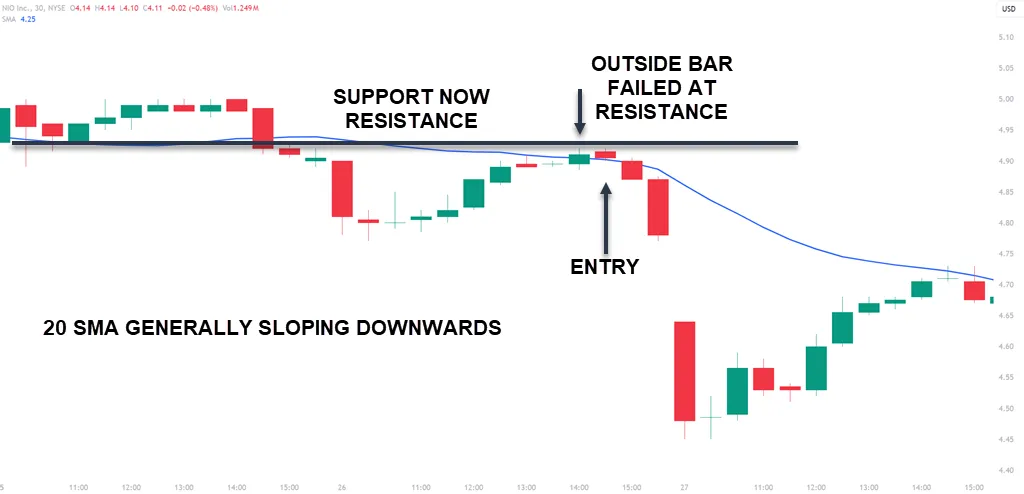
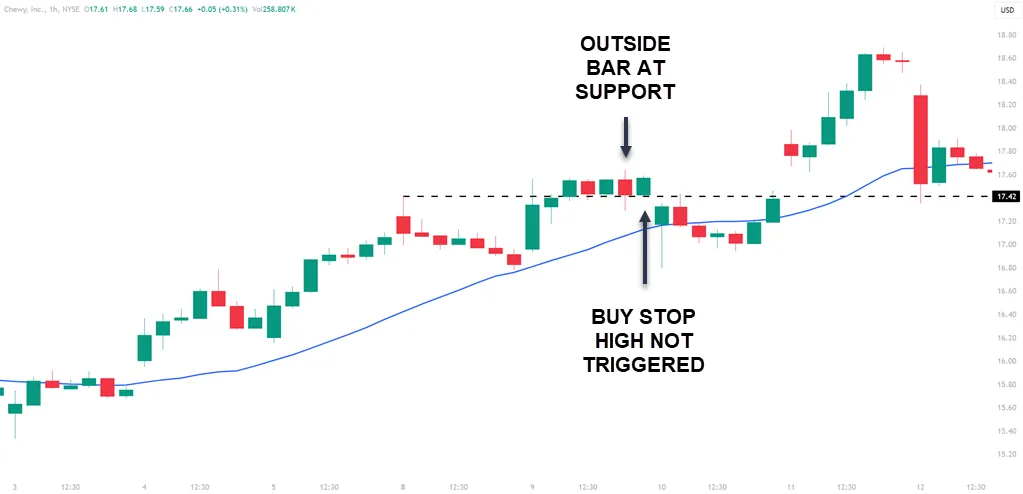
Not all trades will trigger because of the buy or sell stop and that will save you many losing trades. This is a one-hour chart and while the outside bar is a good one, the next candle would have your buy-stop set.
The price pulls back deeper than where the stop loss would have been placed. The buy/sell stop is a great order entry tool that all traders may want to consider using.
Limitations, Risks, and Psychological Challenges
To do well in contrarian trading, you need to accept the challenges it presents, including its limitations, risks, and psychological barriers.
- Managing risk is vital to safeguard against losses caused by prolonged trends and poorly timed entries.
- Building emotional strength is important for handling the mental hurdles of going against the majority and handling emotions like fear and greed.
- Precision in timing is key in contrarian trading to seize opportunities created by market inefficiencies and avoid missing out on profitable trends from following the crowd.
Contrarian trading comes with limitations such as the need for accurate timing, the risk of overlooking external factors impacting market sentiment, and the possibility of overlooking lucrative trends. By focusing on effective risk management, maintaining discipline, and keeping sight of long-term objectives, you can effectively tackle the psychological obstacles inherent in contrarian trading.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Studying real-world examples and case studies can offer valuable insights into how contrarian trading strategies work in practice. For instance, looking at past events like the Dot-Com Bubble and Housing Bubble can illustrate the effectiveness of contrarian approaches. These case studies demonstrate how contrarian traders were able to take advantage of market overreactions and pinpoint pivotal moments to profit from changes in market sentiment.
In the Dot-Com Bubble, contrarian traders identified when the market was overreacting and found opportunities at turning points. This showcases the importance of understanding investor psychology and being able to act against the crowd.
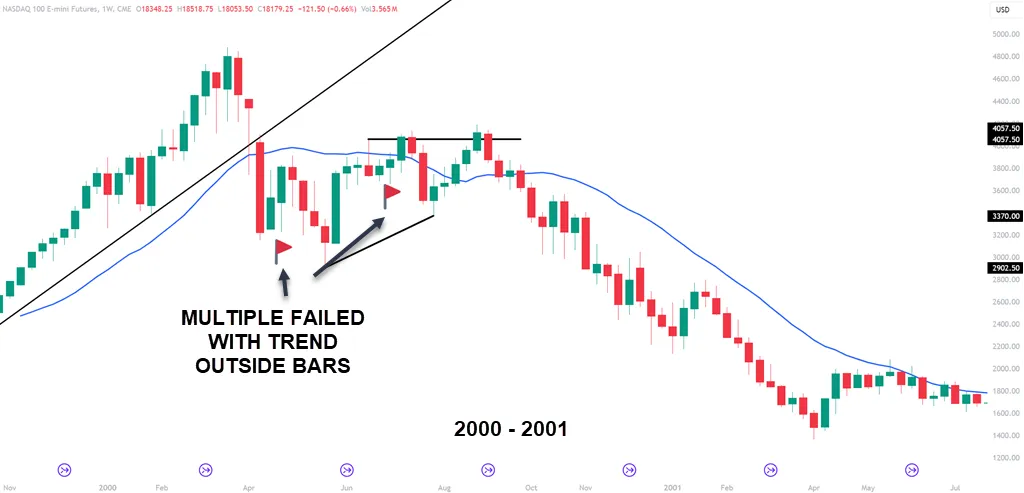
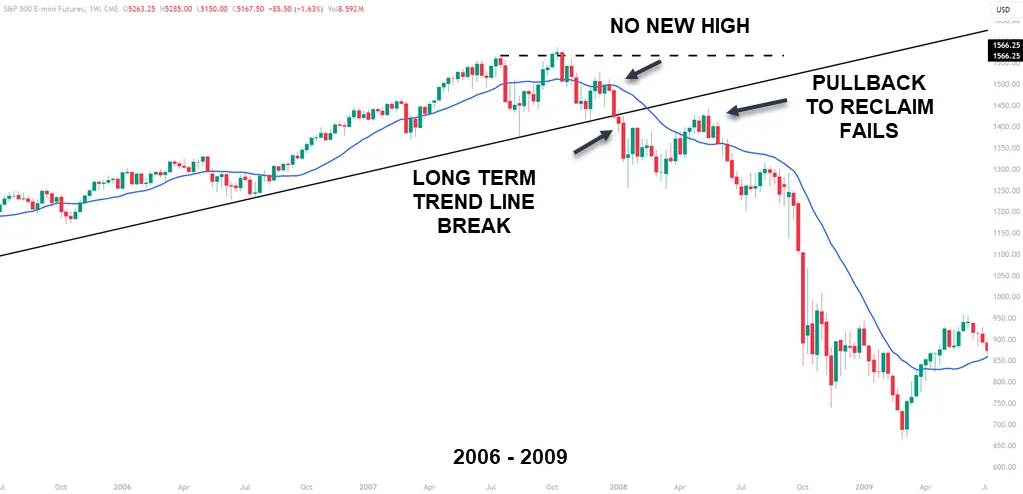
The NQ showed a trend line break and multiple with trend outside bar failures. An outside bar in the direction of the trend usually points to continued price movement. In the case of the NQ in 2000, nothing could save the downmove that was to come.
During the Housing Bubble, contrarian strategies allowed traders to benefit from shifts in market sentiment. By exploiting market inefficiencies, they were able to make informed decisions that led to profitable outcomes.
In times of financial crises, contrarian indicators can be effectively used to capitalize on irrational behavior in the market. This highlights the importance of staying rational and objective when others are panicking.
Advanced Concepts and Variations
Look deeper into the outside bar failure pattern by exploring advanced concepts and variations to improve your contrarian trading strategies and the results. Adding indicator combinations can boost your confidence when trading this pattern. By utilizing various technical indicators like moving averages, contrarian traders can improve their analysis and decision-making process.
Trying out different timeframes is another useful technique to tailor the setup to your trading style. This flexibility enables you to adjust to diverse market conditions and timeframes effectively.
Incorporating volume confirmation can strengthen the outside bar failure pattern’s reliability. Examining volume alongside this pattern can provide valuable insights into the conviction behind potential market reversals.
It’s been said a lot but advanced risk management techniques to limit losses and maximize profits while trading the outside bar failure pattern is key. By adding these advanced concepts and variations, you can refine your contrarian trading strategy and potentially boost your success rate in the market.
Conclusion
In contrarian trading, mastering the Outside Bar Failure Pattern involves understanding market dynamics, using indicators effectively, and managing risks with precision. By staying logical and objective, traders can take advantage of profitable opportunities and navigate pattern failures successfully.
To succeed in contrarian trading using this pattern, it’s crucial to focus on volume confirmation and employ advanced strategies. With dedication and practice, achieving success in contrarian trading is within reach.
FAQ
What is an Outside Bar pattern and how is it defined?
An Outside Bar is a candlestick pattern where the entire range of the current bar completely engulfs the range of the previous bar. This means the current bar has a higher high and a lower low than the prior bar, indicating increased volatility in both directions.
How can the failure of an Outside Bar pattern be traded for potential reversals or continuations?
The failure of an Outside Bar pattern occurs when the price breaks out of the Outside Bar’s range but quickly reverses back inside the range. This can signal a potential reversal of the breakout direction or a continuation of the prior trend. Traders look to enter in the direction of the reversal or continuation.
What are some common trading strategies and setups for trading the Outside Bar Failure pattern?
Common strategies include fading the initial breakout by entering in the opposite direction of the breakout when the price reverses back inside the Outside Bar range. Other setups use the Outside Bar Failure as a continuation pattern by entering in the direction of the prior trend after the failure.
How does the Outside Bar Failure pattern relate to other candlestick patterns like Inside Bars, Fakeys, and Pin Bars?
The Outside Bar Failure is closely related to patterns like Inside Bars, where price ranges contract before a potential breakout. A Fakey is a false breakout from an Inside Bar range. Pin Bars are also similar, with a long wick showing the rejection of prices in one direction. All these patterns can signal reversals.
What are the advantages and limitations of trading the Outside Bar Failure pattern?
Advantages include the ability to catch potential reversals or continuations early with a defined risk. Limitations are that false breakouts can occur, so other confirmations like support/resistance tests or candlestick patterns may be needed to increase the pattern’s reliability.