- March 19, 2018
- Posted by: Mark S
- Category: Cryptocurrencies
November 1, 2018 is the 10 year anniversary of a revolution that has rocked the way many conduct business.
This is the date when Satoshi Nakamoto posted his research paper to a small group of cryptography enthusiasts on an obscure website.
Nakamoto’s paper described a form of digital money that was completely free of government oversight and 100% detached from the fiat currency system.
The name of his digital currency was called bitcoin.
Nakamoto officially unleashed his new digital currency into the world on January 3, 2009, by mining 50 bitcoins. Nobody could have imagined at the time how bitcoin has changed the way we think about money, along with its ability to disrupt our entire fiat currency system.
Although bitcoin has been in existence almost a decade, digital currencies are still in their infancy stage. We are just beginning to realize the true potential of Nakamoto’s discovery.
Digital Currency Choices Expanded
During the past few years, several new digital currencies have arrived on the scene. Many of these new currencies are trying to ride the wave of this new frontier just as technology piggybacks as those that came before.
The vast majority of these currencies will become worthless similar to many of the dotcom stocks during its mania phase.
However, some of these digital currencies have true disruptive potential. In fact, a few could eventually replace bitcoin as the leader in digital currency hierarchy.
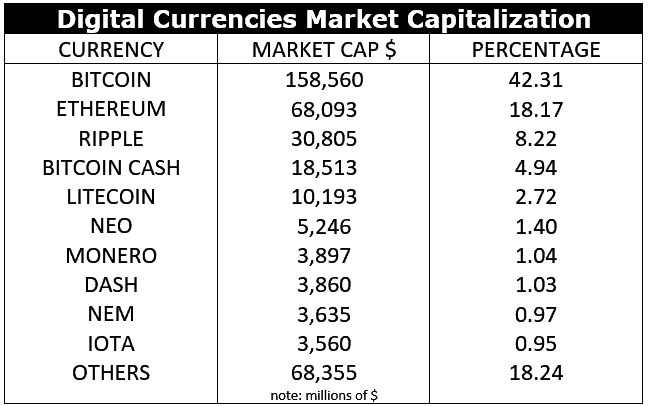
King Of Cryptocurrency Challengers
Let’s run down the list of several digital currencies that have a chance of toppling Bitcoin as the king of crypto
Ethereum (ETH)
The basic concept of Ethereum was first introduced in a 2013 white paper by Vitalik Buterin, a Russian born computer programmer.
In layman’s terms, Ethereum is an open software platform based on blockchain technology that enables developers to build decentralized applications. Prior to the introduction of Ethereum, building a decentralized application was virtually impossible for most developers due to complex issues involving coding, cryptography and mathematics.
Thanks to the development of Ethereum, developers have the necessary tools to create decentralized applications by removing much of the “heavy lifting.”
Many digital currency enthusiasts are constantly comparing Ethereum to bitcoin. In reality, there are more differences between Ethereum and bitcoin than similarities.
The one common denominator between Ethereum and bitcoin is that both are part of a distributed public blockchain network. However, that’s where the similarities end.
For example, bitcoin offers one particular application of blockchain technology, a peer-to-peer electronic cash system that enables online bitcoin payments. The Bitcoin blockchain is used to track ownership of the digital currency (i.e. bitcoin).
However, the Ethereum blockchain focuses on running the programming code of any decentralized application. Ethereum miners are not mining for bitcoins.
Instead, these miners work to earn Ether, a type of crypto token that fuels the entire Ethereum network. In addition to being a trade-able digital currency, ether is also used by application developers to pay for transaction fees and services on the Ethereum network.
The exciting part of the Ethereum blockchain is its capability to build smart contracts.
Remember, Ethereum provides developers with the necessary tools to easily create different applications. Therefore, developers can produce smart contracts for an unlimited amount of different uses.
The list includes such things as:
- insurance contracts
- copyright protection for music and publishing
- delivery services
- financial transactions, land and title contracts
- supply chain management, medical records and many other areas.
During the past several months, Ethereum has increased dramatically in terms of popularity among traders and within the entire community of digital currency enthusiasts. Going forward, Ethereum has a tremendous amount of upside potential.
Ripple (XRP)
Ripple was launched in 2012 by a team of former bitcoin developers.
Unlike bitcoin, Ripple is more than a digital currency. It actually has two distinct features. Ripple is a real-time gross settlement system (RTGS) and a currency exchange & remittance network. Based on the fact that Ripple has RTGS capability, it can enable secure and instant global financial transactions of any size with no chargebacks.
As an added bonus, the cost of each transaction on the Ripple network is practically free (.000001 XRP).
Many industry experts claim Ripple could be the logical successor to bitcoin based on the fact that it has been well received in the financial community. Unlike bitcoin, any currency can be transferred or traded through the Ripple system. Ripple has often been described as “a digital version of Western Union without the heavy fees.”
Since its inception, the Ripple development team has focused its efforts on improving financial transactions and streamlining the transfer of money. In 2013, Ripple Labs was launched in order to create several different development projects with some of the “heavy hitters” in the financial services industry.
- In January 2014, Fidor Bank (based in Munich, Germany) became the first bank to use the Ripple protocol.
- The first American banks joined the Ripple network in September 2014, when Cross River Bank and CBW Bank began using Ripple for intrabank transfers.
In 2015, Ripple Labs announced a major partnership with Earthport, a global payments service provider. Specifically, Ripple’s software was combined with Earthport’s payment services system in an effort to create a better user experience for Earthport’s clients. The company operates in 65 countries and includes Bank of America and HSBC as its two largest clients.
Throughout 2015 and 2016, Ripple (the company) gained international exposure by opening offices in London, Luxembourg and Sydney, Australia. Several companies within these countries have announced partnerships and joint agreements with Ripple.
In September 2016, Ripple increased its presence on the global stage by announcing the creation of the first inter-bank group for global payments based on distributed financial technology. The network is known as the Global Payments Steering Group (GPSG).
The purpose of the group is to “oversee the creation and maintenance of Ripple payment transaction rules, formalized standards for activity using Ripple, and other actions to support the implementation of Ripple payment capabilities.”
A few members of the network include:
- Bank of America
- HSBC
- Merrill Lynch
- Royal Bank of Canada
- Standard Chartered.
Ripple has risen through the ranks of the digital currency hierarchy and in less than five years, it has become one of the leaders within the industry. When the dust finally settles in the digital currency universe (probably during the next few years), it certainly appears Ripple will be one of the survivors.
Litecoin (LTC)
Litecoin is a peer-to-peer cryptocurrency released by Charlie Lee, a former Google employee. The launch date was October 13, 2011. LTC has often been called “the poor man’s version of bitcoin” based on the fact that it is cheaper and more readily available.
In terms of specific technical details, Litecoin is nearly identical to bitcoin.
It is based on the same open source code behind bitcoin. However, Litecoin generates blocks four times faster than bitcoin. Therefore, it can confirm the legitimacy of transactions much quicker as well as process the transactions at a higher speed. A Litecoin block can be processed every 2.5 minutes, compared to 10 minutes for bitcoin. This allows Litecoin to target merchants who need a large volume of small transactions to be processed relatively quickly.
One of bitcoin’s redeeming qualities among investors is its limited supply. Bitcoin is capped at 21 million tokens. Litecoin also enjoys a similar feature. LTC is limited to 84 million coins. This helps preserve the intrinsic value of Litecoin.
In regard to mining LTC and storing the digital currency in a wallet, the process is very similar to bitcoin. Additionally, all Litecoin transactions within its blockchain are public and searchable. The same holds true with all other public cryptocurrencies.
At the end of the day, Litecoin is basically a spinoff of bitcoin. Most likely, the long-term success of Litecoin will be determined by its “big brother,” bitcoin.
Dash (DASH)
Dash is an open source peer-to-peer cryptocurrency developed by Evan Duffield, a computer programmer from Arizona. The launch date was January 18, 2014.
Early investors in Dash may remember the digital currency by its original name, XCoin. The name was later changed to DarkCoin, and finally rebranded as Dash in March 2015.
Dash offers a few unique features which distinguishes it from bitcoin and other peer-to-peer digital currencies. It offers instant transactions, private transactions and operates as a self-funding model.
Instant transactions are known as InstantSend. As the name implies, this service allows users to send Dash instantly to other peers. InstantSend was developed with the intent to attract business merchants to accept Dash as a method of payment.
The chief complaint within the merchant industry was the slow transaction speed of bitcoin. Dash solves this problem with InstantSend.
In terms of privacy, Dash offers a unique function known as PrivateSend, a coin-mixing service that adds privacy to transactions by combining identical inputs from multiple users into a single transaction. Many users prefer PrivateSend because of its anonymity feature.
The majority of cryptocurrency models are established as non-profit entities. Dash operates under a self-funding model. The Dash Core Team has 30 full-time employees and 20 part-time employees. All employees are paid from Dash’s budget system, thereby reducing the need of donations or sponsors.
The acceptance of outside donations by other cryptocurrency projects has always been a cause of concern within the digital currency community. Purists within the community claim that donations and sponsorships create a conflict of interest, usually resulting in unnecessary arguments.
At the end of the day, most digital currency enthusiasts agree that donations and other outside influences are harmful to the cryptocurrency movement.
Many users are drawn to Dash because of its self-funding mechanism and added level of anonymity. It certainly appears that Dash has addressed a few of the problems plaguing bitcoin users. The future looks bright for Dash.
Other Digital Currencies Contenders
- Bitcoin Cash
- Cardano
- Stellar
- EOS
- NEO
- NEM
- Monero
- IOTA
